The most important antitrust lawsuits against Google shake the American tech landscape.
Accused of manipulating the online search and advertising market, the giant faces unprecedented legal challenges.
Unfavorable decisions mark a potential turning point for the digital industry.
For several years, Google has been at the center of controversies regarding its business practices. The two main lawsuits, filed in 2023 and 2024, highlight strategies aimed at maintaining its dominance at the expense of competitors. Judges Amit Mehta and Leonie Brinkema have issued rulings that could lead to the company’s breakup. The outcome of these cases will determine the future of Google and could redefine the rules of the game in the tech sector.
Table of Contents
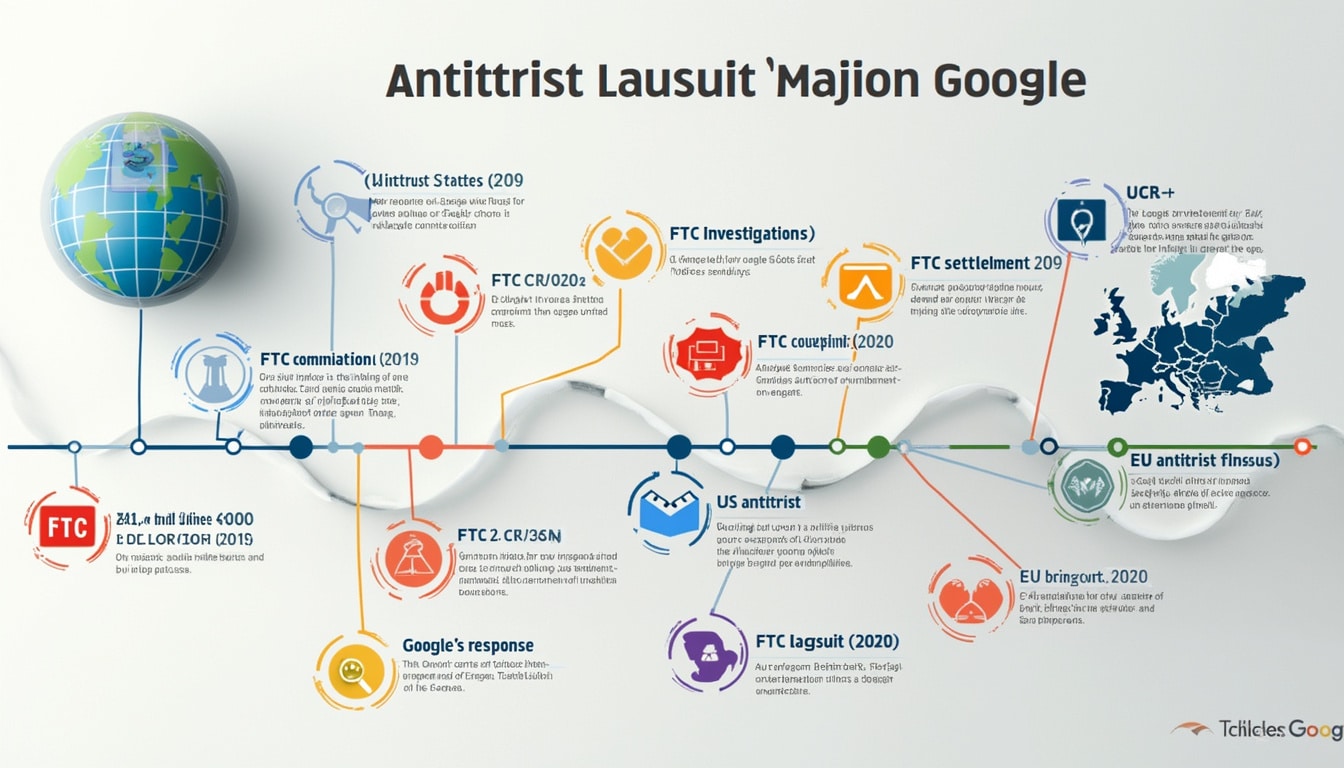
ToggleTimeline of antitrust lawsuits against Google in the United States
For several years, Google has faced severe accusations regarding its dominant position in the market. The two biggest antitrust lawsuits filed against the tech giant target its search and advertising operations respectively. These cases, the most significant in their category this century, have concluded with unfavorable rulings for the company. This article outlines the key milestones of these lawsuits and their implications.
Why is Google accused of monopoly in the search sector?
The dominance of Google in the field of online search has raised concerns about its ability to maintain this position at the expense of competition and consumers. The U.S. government has filed two antitrust lawsuits against Google, claiming that the company manipulated the market to exclude its competitors and harm the public. The first lawsuit, launched in September 2023, focused on Google’s search practices.
According to prosecutors, Google allegedly used exclusive contracts and strategic acquisitions to strengthen its grip on the search market, thus limiting opportunities for other players to thrive. This situation is reminiscent of the famous antitrust case against Microsoft at the beginning of the century, where the software giant was also accused of monopolistic behavior. Google’s ability to maintain its dominant position raises crucial questions about fair competition and innovation in the digital sector.
What were the key milestones of the first antitrust lawsuit on search?
The initial antitrust lawsuit against Google, focused on its search activity, underwent several key stages. In September 2023, the trial’s commencement phase marked the official launch of the accusations. For over a year, hearings followed one another, culminating in May 2024 with the final arguments presented by the Department of Justice.
In August 2024, federal judge Amit Mehta issued an unfavorable ruling for Google, concluding that the company had engaged in anti-competitive behavior to protect its monopoly in search. This ruling paved the way for a three-week hearing scheduled to begin on April 21, 2025, where corrective measures, such as the possible breakup of Google, will be examined.
Key witnesses, including Google’s CEO Sundar Pichai, were questioned about the relationships between Google and other tech giants like Apple. These testimonies revealed unprecedented details about Google’s strategies to maintain its position, including exclusive contracts with hardware manufacturers like Apple to be the default search engine.
What does the second antitrust lawsuit centered on advertising involve?
The second antitrust lawsuit against Google, launched in September 2024, specifically targets its practices in the online advertising sector. Accused of monopolizing the advertising technology market, Google is alleged to have used exclusionary strategies to stifle competitors and control the most widely used advertising tools and exchanges.
During the 15 days of trial, arguments shed light on Google’s strategic acquisition of companies like DoubleClick in 2008, thereby allowing the company to consolidate its grip on the market. In April 2025, Judge Leonie Brinkema issued a ruling against Google, characterizing its practices as “illegally monopolized.” Possible remedies include splitting off Google’s advertising products or implementing significant changes to its business practices.
This lawsuit strongly resonates with the Microsoft antitrust case, where similar measures such as the breakup of the company had been considered if the charges were upheld. Google is considering appealing these decisions, thus prolonging the legal battle.
What impacts could these judicial decisions have on Google?
The unfavorable rulings in both antitrust lawsuits pose a serious threat to Google’s future. If regulators decide to split the company, this could fragment its various branches, including search and advertising, thereby reducing its overall influence in the digital marketplace. In its ruling on the advertising lawsuit, Judge Brinkema indicated that Google’s exclusionary behavior had significantly harmed publishers, the competitive process, and consumers.
The U.S. government, represented by Attorney General Merrick Garland, hailed these victories as historic gains for the American people, stating that no company, no matter how powerful, is above the law. These decisions could also set a precedent for other large tech companies facing similar accusations, thus strengthening antitrust regulation in the United States.
The possibility of splitting Google recalls the case of Microsoft, where such a measure had been considered to encourage healthier competition. For Google, these decisions could not only lead to a reduction in its size and power but also compel the company to reevaluate its business strategies and relationships with partners like Apple and Samsung.
How do the antitrust lawsuits against Google fit into the historical context of tech regulations?
The antitrust lawsuits against Google are part of a long tradition of regulating large tech companies in the United States. The most emblematic case remains that of Microsoft in the early 2000s, where the government sought to limit the company’s power in the software sector. Like Microsoft, Google faces accusations of monopolistic behaviors that could have major consequences for its organization and operations.
These lawsuits reflect an increased awareness among regulators regarding the potential impacts of large tech companies on the market and competition. By specifically targeting Google’s practices in search and advertising, the U.S. government aims to establish a balance where innovation and competition can thrive unhindered.
What are the upcoming developments to watch in these antitrust lawsuits?
As Google plans to appeal the decisions rendered by Judges Mehta and Brinkema, the coming months will be crucial in determining the future of the company. Upcoming hearings, including a four-week session scheduled for April 2025 to decide on corrective measures, will be decisive. These hearings will aim to determine whether Google should be divided or if further restrictions should be imposed on its operations.
Moreover, the outcome of these lawsuits could influence future antitrust legislation and the way large tech companies are regulated. Other market players are closely monitoring these developments, as they could also impact their own business relationships and market strategies.
In conclusion, the antitrust lawsuits against Google mark a significant step in the regulation of tech giants and could redefine competition standards in the digital sector.
For more information about the details of these lawsuits and their implications, check out the following articles:
- The ultimate defense in the Google antitrust trial over advertising technology
- The ultimate plea of the defense in the Google antitrust trial over advertising technology
- The reasons behind the update of Google’s privacy sandbox
- Is Google a monopoly? The second antitrust trial of the U.S. Department of Justice, this time focused on advertising technology
- Two weeks of antitrust trials against Google: a recap of the key events
ZD Tech : Procès antitrust en Europe : pourquoi Google rit, pourquoi Qualcomm pleure https://t.co/qkfjtbNgWl
— ZDNet.fr (@zdnetfr) September 19, 2024